Cannabidiol, or CBD for short, is a compound that’s found in both marijuana and hemp plants. It’s making headlines because of its potential health benefits minus the THC-produced “high” you get when you smoke or ingest marijuana, whether for medical or recreational purposes. In fact, in addition to the fact that CBD won’t get you high, it also has very few side effects, something which is pretty rare in a substance with so many medical possibilities.
Research is Promising
Much of the clinical research on CBD to-date has been conducted or sponsored by the U.S. government, and in general, the news has been extremely promising. A recent survey found that customers are using CBD to help with ailments such as chronic pain, anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, PTSD, MS, and inflammation.
Why Study Cannabidiol?
CBD and THC are the two main substances found in cannabis plants, although there are many others in smaller concentrations. Because these two substances are the dominant ingredients, it’s logical that they would be the most researched and studied. Anecdotal “evidence” of the usefulness of CBDs has been around for thousands of years (dating back to 2737 BC), and modern scientific research is providing factual evidence through controlled studies, which demonstrates that this anecdotal evidence cannot be relegated to the category of “old wive’s tales”!
The Endocannabinoid System
Did you know that your brain and nervous system have receptors for cannabidiol? It’s a fact, and it’s one of the reasons that CBD holds such promise for so many medical conditions. If your body didn’t have these receptors, you wouldn’t get high when you smoke marijuana nor would CBDs have any healing benefits at all.
Endocannabinoids are molecules produced naturally by the body (“Endo means “within”) that bind to and “activate” cannabinoid receptors, just like the plant-based cannabinoids found in marijuana and hemp do. Without getting too scientific, they exist within your body to keep things balanced. The body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) is simply a molecular system for helping maintain homeostasis, which basically means that your physiological system is operating “just right” — just as they should be to perform a multitude of functions within your body.
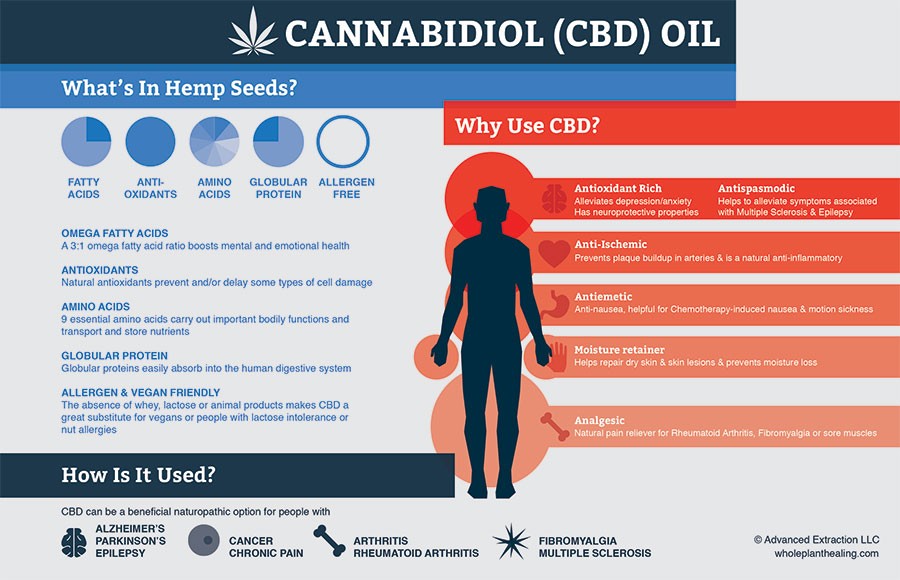
Image Source – wholeplanthealing
How CBD is Extracted
CBD can be extracted from both marijuana and hemp. For a product to be legal in all 50 states, the CBD must be extracted from industrial hemp which only has a negligible amount (0.3%) of THC in it — not enough to get anyone “stoned”.
The substance is extracted from the stems and leaves using Ethanol and/or CO2, both clean and efficient methods when extracting CBD for human consumption. Ethanol is commonly used for extracting CBD from large quantities of hemp, while CO2, which is a slightly more sophisticated method where the plants are filtered through a series of chambers that control both temperature and pressure, is generally used when smaller quantities of hemp are being processed.
How Cannabidiol is Administered
There are many products available today which are CBD based and come in topical form, as oils, as supplements, and even in edible form.
Look for Hemp-Based CBD Products
CBD products produced from hemp have a reputation for being safe and effective and are legal since they contain only trace amounts of THC. However, it’s always a good idea to check with your doctor to make sure that they won’t interact in a negative way with any medication you may be taking.